What are we talking about when we talk about systems? (A primer on systems theory)

I created that video partly because I was trying to increase the reach for the Centre’s work on social media. We’re starting a new course soon, which means that I have do some marketing, and since my strengths do not lie in the kind of content-creation that gets attention these days, I was trying to stretch myself into a new way of communicating.
Ironically, when I tried to boost the post on Facebook so that more people would see it (that’s the way Facebook makes money off of small businesses like ours – it only puts our stuff in front of very limited audiences unless we pay for the post), it got rejected. Apparently, it didn’t comply with their policy about “social issues, elections or politics” (probably because I used the words “white supremacy” in the video).
The whole thing really makes me laugh, partly because it feels like a message from the universe saying I should stick with what I do well, and partly because I got rejected by a representative of one of the systems I was naming in the video – namely, capitalism (in the form of social media). Luckily, I know better than to measure my worthiness by their measurement!
***
The above is a prelude to what I actually want to write about in this post – systems thinking. It occurred to me, after posting the video, that perhaps it would be worthwhile to take a step back and explain what I’m talking about when I talk about the “systems” that measure us. One of the goals of my new course, Know Yourself, Free Yourself is to help people see the systems that they are a part of so that they can learn to live in a more liberated relationship with those systems (particularly those that cause harm). But maybe, before you can see those systems, you have to first have a basic understanding of what you should be looking for?
Systems Theory is a vast field of study, with many different tentacles, and it’s a little slippery – kind of like an octopus that keeps slipping out of grasp just when you think you’ve got it – so I won’t do a great job of clarifying it in this short blog post, but I’ll at least give you a primer, as I understand it. While first introduced as a biological concept, it has been expanded as a way to understand families, workplaces, cultures, and beyond.
According to Systems Theory, anything that happens within a system must be examined with that system in mind because every part of a system impacts the whole. In other words, you can’t separate an individual from the system they live in, and, at the same time, the system is nothing without the individuals that create and maintain it.
Let’s consider the human body as an example of a system. The hand might imagine itself as separate and independent of the feet, but if the hand reaches for a banana, it can only pick it up as long as the feet don’t revolt and move the body to another room. Neither the hand nor the foot can function unless the muscles, heart, skin, and brain cooperate. And then, because they are all interdependent, those things can’t function as long as the hand is being kept away from the banana that will fuel the whole body.
You can’t examine the hand without considering what it is attached to (and fed by), and you can’t examine the body without recognizing that the hand is part of what makes it a body.
Now extrapolate that out to consider the way that we as individual bodies are connected to the families, cities, cultures, religions, etc. that we are a part of. None of us can be seen entirely separate from these systems, and these systems don’t exist if none of us are willing to contribute to them. Consider a church, for example. A person who’s a member of that church is being influenced by that church and, if you want to truly understand that person, you have to zoom the lens out to see what beliefs, biases, and relationships are part of that person’s life because of the church they’re part of. At the same time, if all of the people who are part of that church walk away from it, the church ceases to exist.
Below is a diagram that shows some of the complexity of the various levels of systems that we are all part of. This model emerges out of Urie Bronfenbrenner’s Bioecological Model of Systems, which focuses primarily on child development, but it can be expanded to all of our social systems.
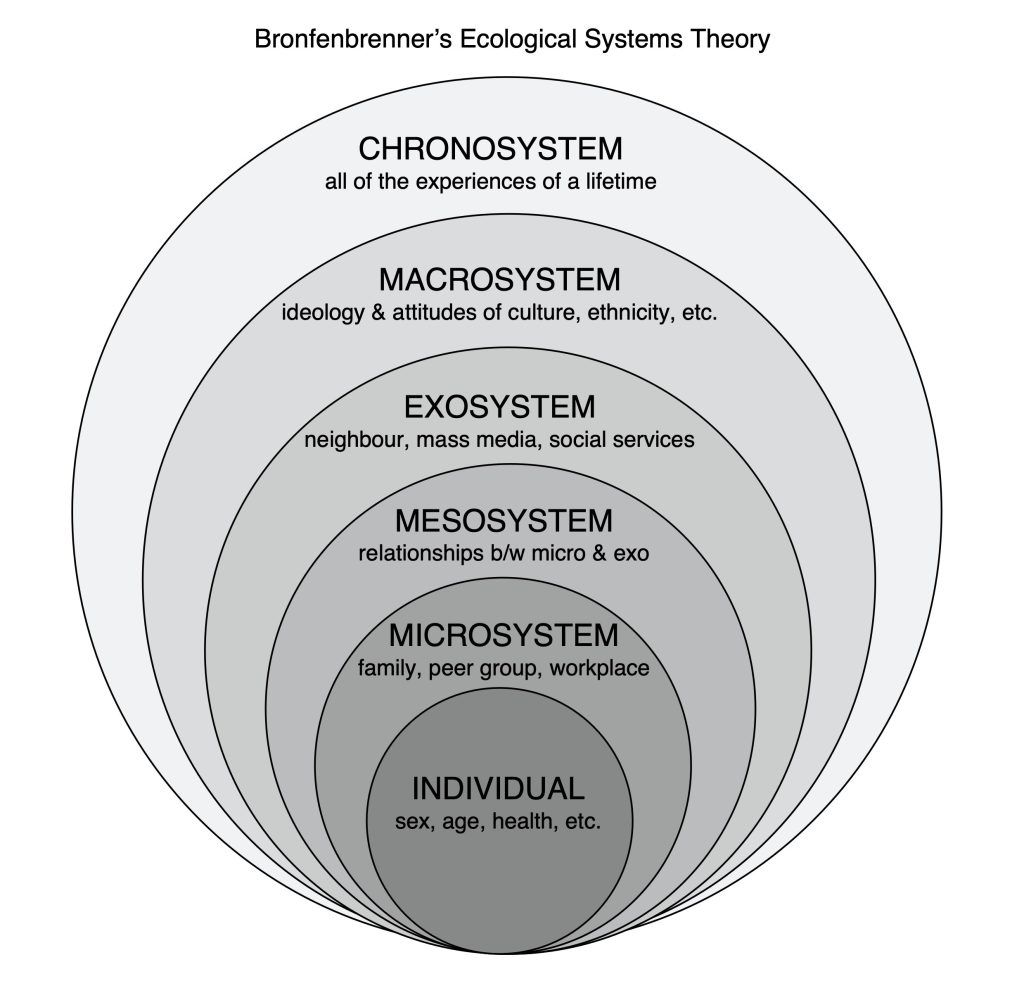
At the smallest level, you are the individual at the centre (with your own system existing within your body). Then you are part of a number of microsystems (your family, school, peer groups, local church, etc.). Next is the mesosystem (which weaves together the relations between microsystems and exosystem – for example, the relations between your family members and their coworkers). Then the exosystem (your neighbours, friends of family, mass media, government agencies, social welfare systems, social media, etc.). Then the macrosystem (attitudes and ideologies of the culture, ethnicity, geographic location, socioeconomic status, etc.). Finally, the chronosystem holds all of the experiences of a lifetime (environmental events, major life transitions, and historical events).
Let’s expand the analysis of the person who’s a member of a local church. Not only is it insufficient to examine that person separate from the church that they’re a part of, it is also insufficient to examine that church separate from the broader systems that it is part of. That local church is likely part of a denomination that shapes the traditions, historical relevance, ideologies, beliefs, and biases of that church. That denomination may have multiple levels of influence, from the localized grouping of churches, up to the global governance structure. It is also embedded within a religion that informs, among other things, what version of God is worshipped and how members of that religion interact with people of other religions. And then there is the neighbourhood, city, country, and region of the world that the local church is located in – all of these things also have influence, meaning that a local church in one country won’t look the same as a local church in another country even if they’re in the same denomination.
At an even broader scale, that local church (and, by extension, each member of the church), is being influenced by what’s at the macrosystems level. This is where things like colonization, patriarchy, white supremacy, classism, racism, and capitalism come into play. A church rooted in the patriarchy, for example, will likely still be led by a man, and where white supremacy is an issue, that man will likely be white. And, here in North America in particular, no church is completely free of the colonization that built our countries.
ALL of these systems are at play in that one individual who is a member of that one local church, and so that person cannot be fully witnessed without recognizing what’s at play. Even when that person leaves that church, the systems will still be at play, especially if the person is unconscious of the way that they’ve been influenced while part of that church. (Also at play will be all of the other systems that individual is part of – family systems, community systems, work systems, etc.)
Systems usually evolve as a way to organize us. A system without some form of organization won’t be able to sustain itself or serve the purpose it’s meant for, and so, if we value a system and find meaning in it, we organize it. Imagine, for example, a school that has no sense of order – nobody is responsible for doing the teaching or clean up and students are allowed to do whatever they please. That’s not education, it’s anarchy. (Some would suggest that it would eventually become a self-organizing system, if the desire for education is great enough.)
The problem is that what organizes us often begins to control us. When we become too rigid to allow a system to evolve, when we put the value of the system above the value of the individuals in that system, and when we embed a measurement of worthiness into a system (what Isabel Wilkerson refers to as Caste), then that system is no longer just organizing us, it’s controlling and measuring us. That’s when we end up with the dominance and oppression of systems like colonization.
Then, when a system begins to control people using dominance and oppression, that system begins to cause trauma in its people. A system that causes trauma becomes a system full of traumatized people and (because what happens at the micro level is also what happens at the macro level) it is therefore a traumatized system. Once you have a traumatized system, it becomes particularly destructive and particularly difficult to change. That’s when you see the levels of brokenness that have been showing up in the world – like climate change, and what’s currently happening in the Ukraine.
A traumatized system (just like a traumatized individual) needs people that can hold space for it while it heals. But the challenge is that EVERYBODY in that system has become traumatized and so it’s difficult to step outside of the system enough to help it with its healing. It becomes a self-perpetuating cycle of trauma.
I am not without hope, though. I have personally witnessed many people, in recent years, who are waking up to this trauma enough so that they can heal it in themselves, and then move themselves far enough outside of the traumatized system so that they can offer healing back to that system and the people in it. These people are learning to work with each other, with the natural world, and with whatever form of spirituality might support them, so that they can work to heal a broken world.
In the Berkana Institute’s Two Loops Model (below), we’re given a hint about what happens when people begin to move away from a traumatized system. The upper loop represents the dominant system, which was once vibrant and alive and served a purpose (the top of the loop). At some point, though, a system’s purpose is fulfilled, and then it needs to complete its cycle so that it can die and make space for a new system. Lots of people resist that system’s death, because it keeps them safe, but some people recognize that the system needs to die and they step away from that system. If those people were traumatized by the dominant system, they must do healing work or they will continue to perpetuate the same trauma that was embedded in the system. As they heal, their imagination becomes reawakened and they become innovators who begin to imagine the birth of something that can replace the dying system. That’s what the bottom loop is for – it represents the evolution of the new system.
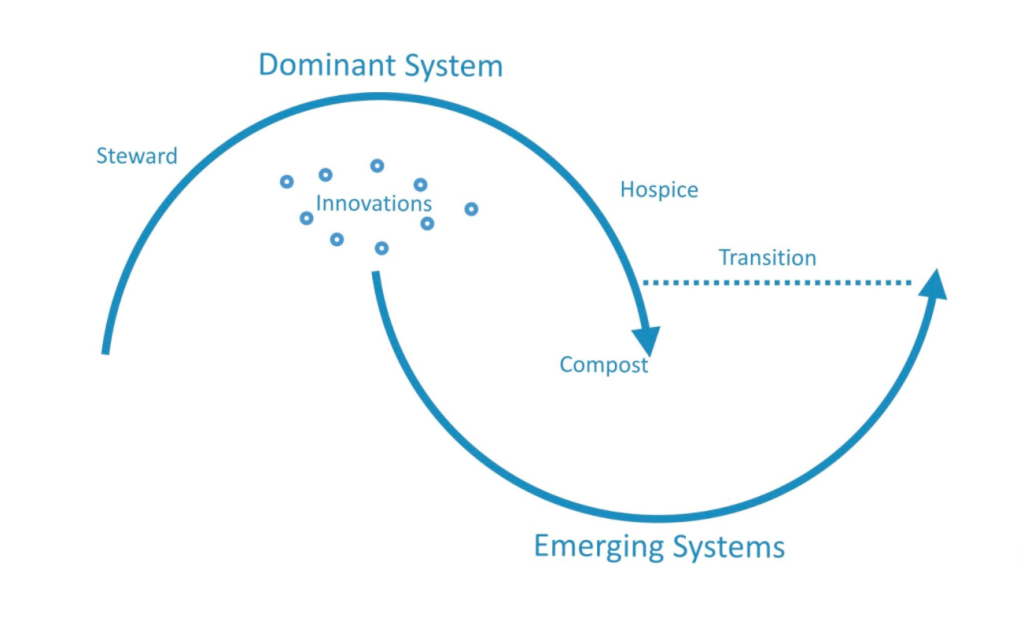
In addition to the innovators, there is also a role for hospice workers – those who are willing to support the hospice work of the dying system. Once the old system has been released, the hospice workers join the innovators.
That’s why I’ve created my new course, Know Yourself, Free Yourself. I want to support those people who are waking up – those who are doing their healing so that they can become hospice workers or innovators (or both). I want to help them see the systems more clearly. I want to walk alongside them as they examine their lineage, trauma, beliefs, biases, and relationship patterns. I want to help them imagine themselves as whole people, apart from the systems that measure and control them. I want us to imagine collective liberation and generative love. I want us to know community, connection, and joy. I want us to set our imaginations free so that we can dream our way into new ways of being.
I hope that you will join me in this. It feels really, really important, and perhaps even urgent. That’s one of the reasons why we’ve created three levels for the registration fee – because we want this program to welcome into the circle people from around the world and from across the socioeconomic spectrum.
I look forward to being in conversation with you.
